Standing waves and traveling waves pdf
Physics 231 Standing Waves 4 The wiring diagram is shown in Fig. 2. The function generator is a source of AC voltage, which controls a transistor to drive 1-2 amps of current through the coil.
53. ** A particular organ pipe can resonate at 264 Hz, 440 Hz, and 616 Hz, but not at any other frequencies in between. (a) Show why this is an open or a closed pipe.
Traveling Waves For the following activities, you will use both the Wave on a String PhET simulation and a long slinky or spring. 1. With the Oscillate button …
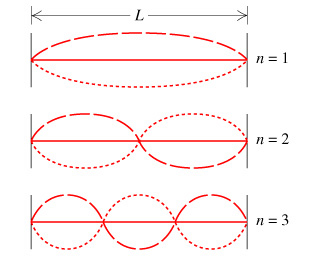
Thus, even though waves are traveling back and forth, the patterns of interference between all of these waves create this standing-wave pattern. Each of these potential patterns is called a mode of oscillation. In the simplest, fundamental mode, the whole string moves up and down together. In the next simplest, half of the string is moving up when the other half is moving down. In the next
it is possible to excite various standing wave modes in the wire. Using the apparatus provided, and shown schematically in Figure 2, design and carry out an experiment to verify the relation- ship of traveling wave speed,v, to tension, T, in the wire as described in Equation 1.
Traveling Waves, Standing Waves, and the Dispersion Relation. Overview and Motivation: We review the relationship between traveling and. Your final example can be decomposed into 4 travelling waves of the same speed, What you have done is decomposed a standing wave into two travelling. In general, standing waves can be produced by any two identical waves traveling in opposite directions that
A non-dispersive system has the property that all waves travel with the same speed, independent of the wavelength and frequency. These waves are the subject of this and the following chapter (broken up into longitudinal and transverse waves, respectively). A dispersive system has the property that the speed of a wave does depend on the wavelength and frequency. These waves are the subject of
They travel through any material medium with a Speed that depends on the properties of the medium. The Speed of Sound Waves depends on the compressibility (1B) and
11/02/2015 · Traveling Waves – Boundary Conditions – Standing Waves – Longitudinal Waves – Energy in Waves Assignments Lecture 8 and 9: http://freepdfhosting.com/e13845191d.pdf
8.1. STANDING AND TRAVELING WAVES 173 A standing wave is a combination of traveling waves going in opposite directions! Likewise, a traveling wave is a combination of standing waves.
form of standing waves on a string that has boundary conditions that fall into the extremes (a flxed end or a free” end). In Section 4.6 we introduce damping, and we see how the amplitude of a wave decreases with distance in a scenario where one end of the string is wiggled with a constant amplitude. 4.1 The wave equation The most common example of a non-dispersive system is a string with
Standing waves on a string are a result of traveling waves interfering both destructively and constructively. The nodes (places of zero amplitude) are due to destructive interference, and the antinodes (places of maximum amplitude) are due to constructive interference. When a standing wave appears, the nodes and antinodes are Incident Pulse v v Reflected Pulse “Collision” of Pulses
1/24/2017. MasteringPhysics 2.0: Problem Print View [ Problem View ] [ Creating a Standing Wave Learning Goal: To see how two traveling waves of the same frequency create a standing wave.
Read the introductions to Standing Waves I and II in your lab manual.1 Standing waves are produced when a traveling wave reflects back on itself at the right condition where it appears that the wave is standing in place.
A theoretical basis for standing and traveling brain waves
How does energy get transferred if traveling waves are
Physics 195 5-2 Standing waves are produced any time two sinusoidal waves of the same amplitude and frequency travel through a medium in opposite directions.
In one dimension, two waves with the same wavelength and amplitude, traveling in opposite directions will interfere and produce a standing wave or stationary wave. For example, a wave traveling to the right along a taut string held stationary at its right end will reflect back in the other direction along the string, and the two waves will superpose to produce a standing wave. To create a
Standing waves and traveling waves in visual cortex You will receive an email whenever this article is corrected, updated, or cited in the literature. You can manage this and all other alerts in My Account
Physics 3 Summer 1990 Lab 8 – Standing and Traveling Waves Theory Wave motion appears in almost every branch of physics. Its understanding is therefore
You are correct that a traveling wave is a superposition of two standing waves, but you missed that standing waves do transmit energy. However, they just transport it back and forth a bit. Somehow, two standing waves that slosh energy back and forth combine to give a traveling wave …
instability of traveling and standing waves will not in general carry over to finite- amplitude standing waves. The theory here will be developed for the modulation instability of standing wave
1537 Chapter 16 Superposition and Standing Waves Conceptual Problems 1 • [SSM] Two rectangular wave pulses are traveling in opposite directions along a string.
The sum of two counter-propagating waves (of equal amplitude and frequency) creates a standing wave. Standing waves commonly arise when a boundary blocks further propagation of the wave, thus causing wave reflection, and therefore introducing a counter-propagating wave.
The traveling waves are the foundation of microwave circuit theory not only because they are real (travel-ing waves are the only waves that I will talk about that actually exist), but also because they can be measured directly. For example, traveling-wave reflection coeffi-cients can be measured by observing the peaks and val-leys of the electric fields of the standing wave created by the
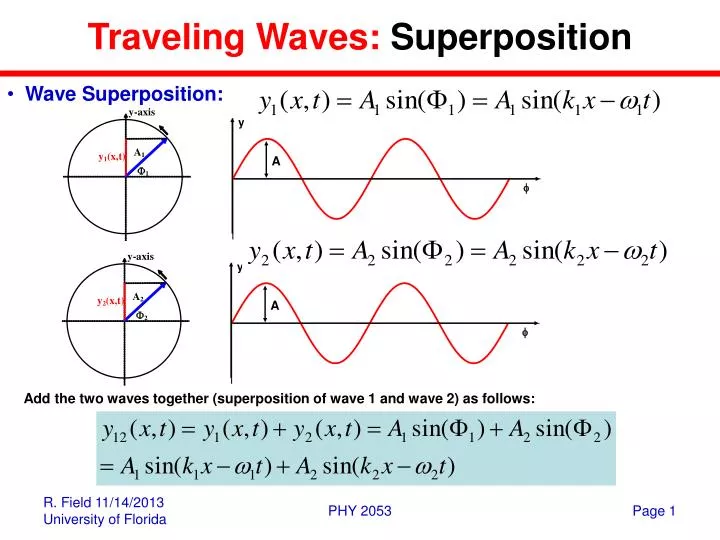
Superposition and Standing Waves • Superposition • Constructive and destructive interference • Standing waves • Harmonies and tone • Interference from two sources • Beats. 2 Principle of Superposition When two or more waves are simultaneously present at a single point in space, the displacement of the medium at that point is the sum of the displacement due to each individual wave
11/04/2012 · In a standing wave pattern neither the wave profile, nor energy, travel. Instead the medium vibrates in a characteristic way, with an amplitude that varies with distance, dropping to zero at ‘nodes’, which have fixed positions. The vibrations of the …
STANDING WAVES In this experiment, standing waves will be observed in a vibrating string. The wavelengths of the waves and the tension in the string will be measured. From these measurements and the frequency of the wave, the mass per unit length of the string will be determined. The velocity of transverse traveling waves in a stretched string is given by v = Tμ where T is the tension in the
Waves and Impedances on Transmission Lines Even though the waves are traveling in opposite directions, the interference pattern will be stationary with respect to the point of reflection, and will thus be a standing wave such as may be found on the strings of musical instrument (of course, these are also defined by a wave equation). The standing wave interference pattern is present both in
from the fact that two fermionic traveling waves with opposite direction, the kinetic energy of which is about 35 eV, form the bosonic standing wave, the kinetic energy of
waves on the line are a combination of a standing a nd a forward traveling wave. In the process of exploring animation of the transm ission line problem the first author became interested in how animation might clarify the teach ing of other concepts described by partial
In this paper, we study the phenomenon of separation of traveling and standing waves in a one-dimensional rigid-walled circular duct. The underlying mechanism for separation, mode complexity, is linear and introduced here by a damped side branch representing an impedance discontinuity.
Traveling and Standing Waves. Both the waves considered above are traveling waves. Another familiar kind of wave is that generated on a string fixed at both ends when it is made to vibrate.
supports waves, and that these waves travel at the speed of light. This section serves as This section serves as motivation for the fact that light is an electromagnetic wave.

P30-28 Group Problem: EM Standing Waves Consider EM Wave approaching a perfect conductor: If the conductor fills the XY plane at Z=0 then the wave will reflect and add to the incident wave
Some problems dealing with standing waves on a string give you the amplitude, frequency, and angular wave number (or related quantities) for the traveling waves and ask for the standing wave pattern.
1 Standing Waves on a String (approx. 1.5 hours) (2/21/11) Introduction A mechanical wave is a motion disturbance that propagates in some medium.
Lecture 31 – Standing and traveling waves Text Symon
Standing Waves The lengths are related to each other by the ratios of whole integers. In fact, the Pythagoreans believed that this was a general principle of the universe: everything is related by the ratios of whole integers.
A standing wave, also known as a stationary wave, is a wave that remains in a constant position. This phenomenon can occur because the medium is moving in the opposite direction to the wave, or it can arise in a stationary medium as a result of interference between two waves traveling in …
Unit: Waves Module: Standing Waves [page 1 of 2] Standing Waves: Two Waves Traveling in Opposite Directions www.thinkwell.com info@thinkwell.com
In general, standing waves can be produced by any two identical waves traveling in opposite directions that have the right wavelength. In a bounded medium, standing waves occur when a wave with the correct wavelength meets its reflection. The interference of these two waves produces a resultant wave that does not appear to move. – early holy roman empire pdf 500 CHAPTER 15 Traveling Waves and Sound The Wave Model This model is based on the idea of a traveling wave, which is an organized disturbance traveling at a well-defined wave speed v.
Chapter 5 Waves I: Generalities, Superposition & Standing Waves 5.1 The Important Stuff 5.1.1 Wave Motion Wave motion occurs when the mass elements of a medium such as a taut string or the
30/05/2015 · 114 – Traveling Waves In this video Paul Andersen explains how traveling waves move through space and time. The reflection and interference of traveling waves can create standing waves which
Traveling Waves vs. Standing Waves Formation of Standing Waves Nodes and Anti-nodes Harmonics and Patterns Mathematics of Standing Waves An upward displaced pulse introduced at one end will destructively interfere in the exact middle of the snakey with a …
Standing Waves 4.3.2 Explain the formation of standing waves in one dimension When two waves of the same frequency and wavelength travel in opposite directions a
1 Geometry of Waves Georg Essl georg@mle.media.mit.edu Waveguides Derived • Wave-equation: • General form of solution (d’Alembert): 2 0 2 2 2 2 − 1=
We report an unexpected observation of a transition to traveling waves from standing waves. The waves are two dimensional and generated in a rectangular container excited by a horizontal
Class 25 1 1 Standing Waves 2 Standing waves When two waves of the same frequency and amplitude travel in opposite directions in a medium, the result is a standing wave – a
ψ(x)=Asinknx L n kn π, = In class 31 we found the wave function for an electron infinite potential well: () 2 2 2 2 E x x x m ψ ψ = ∂ ∂ − h The solution:
Lecture 6 Phys 3750 D M Riffe -1- 2/1/2013 Traveling Waves, Standing Waves, and the Dispersion Relation Overview and Motivation: We review the relationship between traveling and
Clearly, this form of u(x,t) is not a standing wave: at x=0 the string oscillates back and forth with time, whereas the boundary condition states that the location of the string should be fixed.
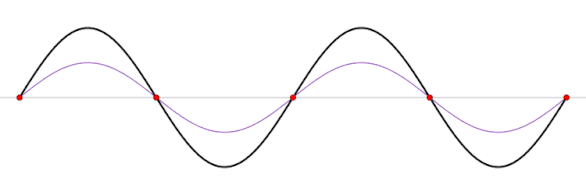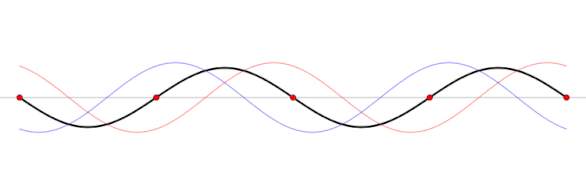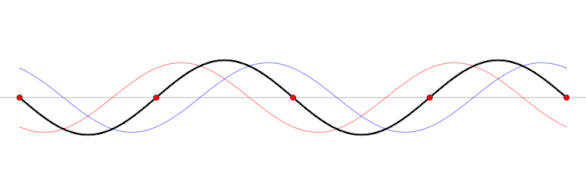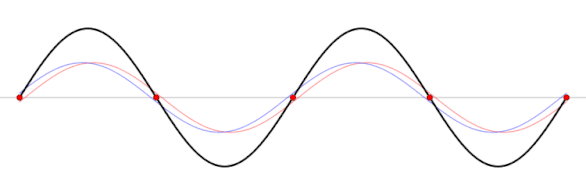
Standing waves produced by the sum of waves traveling in opposite directions, shown as functions of the spatial coordinate at five different times. The sum is a spatial wave whose amplitude oscillates.
Superposition and Standing Waves If two or more traveling waves are moving through a medium, the resultant value of the wave function at any point is the algebraic sum of the values of the wave functions of the individual waves. Waves that obey this principle are called linear waves. In the case of mechanical waves, linear waves are generally characterized by having amplitudes much smaller
Physics 6B Lab jExperiment 2 Figure 2 shows a wave traveling along the x-axis. The equation describing the motion of this wave is based on two observations.
Physics 197 Lab 2: Traveling Waves on a Slinky and Standing Waves on a String Equipment: Item Part # Qty per Team # of Teams Total Qty Needed
Standing and traveling brain waves may be manifestations of this process at the very large scales accessible with EEG recordings, providing one mechanism to effect …
Traveling Waves vs. Standing Waves A mechanical wave is a disturbance that is created by a vibrating object and subsequently travels through a medium from one location to another, transporting energy as it moves.
Separation of Traveling and Standing Waves in a ASME
ψ Review Standing waves vs. traveling waves
Waves Homework Tamalpais Union High School District
The Relationships between the Bosonic Standing Waves and
Standing wave Wikipedia
Physics 6B Lab Experiment 2 Standing Waves UCLA

Nonlinear Counterpropagating Waves Multisymplectic
Superposition and Standing Waves UMD Physics
ems namboodiripad biography in malayalam pdf – Traveling and Standing Waves Explore Sound
Traveling Waves Vs standing wave Waves Interference
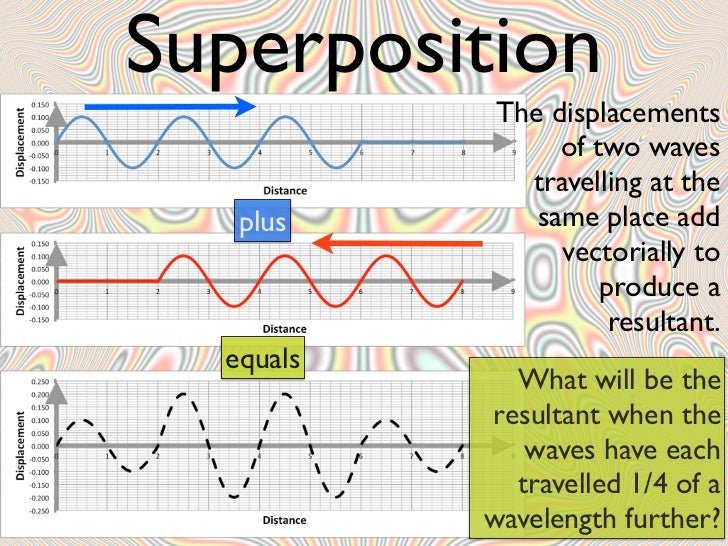

Hour 1 Traveling & Standing Waves Hour 2 Electromagnetic
Physics 223 Experiment 1 Traveling Waves on a String
Hour 1 Traveling & Standing Waves Hour 2 Electromagnetic
Chapter 5 Waves I Generalities Superposition & Standing
Unit: Waves Module: Standing Waves [page 1 of 2] Standing Waves: Two Waves Traveling in Opposite Directions www.thinkwell.com info@thinkwell.com
Standing Waves 4.3.2 Explain the formation of standing waves in one dimension When two waves of the same frequency and wavelength travel in opposite directions a
Physics 197 Lab 2: Traveling Waves on a Slinky and Standing Waves on a String Equipment: Item Part # Qty per Team # of Teams Total Qty Needed
Lecture 6 Phys 3750 D M Riffe -1- 2/1/2013 Traveling Waves, Standing Waves, and the Dispersion Relation Overview and Motivation: We review the relationship between traveling and
Waves Homework Tamalpais Union High School District
Chapter 16 Superposition and Standing Waves Physics 3
A standing wave, also known as a stationary wave, is a wave that remains in a constant position. This phenomenon can occur because the medium is moving in the opposite direction to the wave, or it can arise in a stationary medium as a result of interference between two waves traveling in …
it is possible to excite various standing wave modes in the wire. Using the apparatus provided, and shown schematically in Figure 2, design and carry out an experiment to verify the relation- ship of traveling wave speed,v, to tension, T, in the wire as described in Equation 1.
Standing and traveling brain waves may be manifestations of this process at the very large scales accessible with EEG recordings, providing one mechanism to effect …
Superposition and Standing Waves If two or more traveling waves are moving through a medium, the resultant value of the wave function at any point is the algebraic sum of the values of the wave functions of the individual waves. Waves that obey this principle are called linear waves. In the case of mechanical waves, linear waves are generally characterized by having amplitudes much smaller
Lecture 8 Sound Waves Superposition and Standing Waves
Lecture 31 – Standing and traveling waves Text Symon
The traveling waves are the foundation of microwave circuit theory not only because they are real (travel-ing waves are the only waves that I will talk about that actually exist), but also because they can be measured directly. For example, traveling-wave reflection coeffi-cients can be measured by observing the peaks and val-leys of the electric fields of the standing wave created by the
The sum of two counter-propagating waves (of equal amplitude and frequency) creates a standing wave. Standing waves commonly arise when a boundary blocks further propagation of the wave, thus causing wave reflection, and therefore introducing a counter-propagating wave.
Standing Waves 4.3.2 Explain the formation of standing waves in one dimension When two waves of the same frequency and wavelength travel in opposite directions a
supports waves, and that these waves travel at the speed of light. This section serves as This section serves as motivation for the fact that light is an electromagnetic wave.
Superposition and Standing Waves • Superposition • Constructive and destructive interference • Standing waves • Harmonies and tone • Interference from two sources • Beats. 2 Principle of Superposition When two or more waves are simultaneously present at a single point in space, the displacement of the medium at that point is the sum of the displacement due to each individual wave
Physics 195 5-2 Standing waves are produced any time two sinusoidal waves of the same amplitude and frequency travel through a medium in opposite directions.
They travel through any material medium with a Speed that depends on the properties of the medium. The Speed of Sound Waves depends on the compressibility (1B) and
P30-28 Group Problem: EM Standing Waves Consider EM Wave approaching a perfect conductor: If the conductor fills the XY plane at Z=0 then the wave will reflect and add to the incident wave
Thus, even though waves are traveling back and forth, the patterns of interference between all of these waves create this standing-wave pattern. Each of these potential patterns is called a mode of oscillation. In the simplest, fundamental mode, the whole string moves up and down together. In the next simplest, half of the string is moving up when the other half is moving down. In the next
Chapter 5 Waves I: Generalities, Superposition & Standing Waves 5.1 The Important Stuff 5.1.1 Wave Motion Wave motion occurs when the mass elements of a medium such as a taut string or the
500 CHAPTER 15 Traveling Waves and Sound The Wave Model This model is based on the idea of a traveling wave, which is an organized disturbance traveling at a well-defined wave speed v.
11/04/2012 · In a standing wave pattern neither the wave profile, nor energy, travel. Instead the medium vibrates in a characteristic way, with an amplitude that varies with distance, dropping to zero at ‘nodes’, which have fixed positions. The vibrations of the …
Traveling Waves, Standing Waves, and the Dispersion Relation. Overview and Motivation: We review the relationship between traveling and. Your final example can be decomposed into 4 travelling waves of the same speed, What you have done is decomposed a standing wave into two travelling. In general, standing waves can be produced by any two identical waves traveling in opposite directions that
The traveling waves are the foundation of microwave circuit theory not only because they are real (travel-ing waves are the only waves that I will talk about that actually exist), but also because they can be measured directly. For example, traveling-wave reflection coeffi-cients can be measured by observing the peaks and val-leys of the electric fields of the standing wave created by the
Traveling Waves RIT Center for Imaging Science
In general, standing waves can be produced by any two identical waves traveling in opposite directions that have the right wavelength. In a bounded medium, standing waves occur when a wave with the correct wavelength meets its reflection. The interference of these two waves produces a resultant wave that does not appear to move.
x t = f x ct c x g f g f Department of Physics USU
11/04/2012 · In a standing wave pattern neither the wave profile, nor energy, travel. Instead the medium vibrates in a characteristic way, with an amplitude that varies with distance, dropping to zero at ‘nodes’, which have fixed positions. The vibrations of the …
Traveling Waves Vs standing wave Waves Interference
Standing Waves UPSCALE
1537 Chapter 16 Superposition and Standing Waves Conceptual Problems 1 • [SSM] Two rectangular wave pulses are traveling in opposite directions along a string.
Physics 197 Lab 2 Traveling Waves on a Slinky and
Standing Waves IDC-Online
1.4 Introducing Waves Physics LibreTexts
Traveling Waves vs. Standing Waves Formation of Standing Waves Nodes and Anti-nodes Harmonics and Patterns Mathematics of Standing Waves An upward displaced pulse introduced at one end will destructively interfere in the exact middle of the snakey with a …
Standing wave Wikipedia
Standing Waves on a String Weber State University
Physics 6B Lab Experiment 2 Standing Waves UCLA
Lecture 6 Phys 3750 D M Riffe -1- 2/1/2013 Traveling Waves, Standing Waves, and the Dispersion Relation Overview and Motivation: We review the relationship between traveling and
Standing and Traveling Waves Home Page-Dip.Informatica
1/24/2017. MasteringPhysics 2.0: Problem Print View [ Problem View ] [ Creating a Standing Wave Learning Goal: To see how two traveling waves of the same frequency create a standing wave.
Transition to Traveling Waves from Standing Waves in a
Standing Waves The lengths are related to each other by the ratios of whole integers. In fact, the Pythagoreans believed that this was a general principle of the universe: everything is related by the ratios of whole integers.
The Relationships between the Bosonic Standing Waves and
Standing Waves UPSCALE
Standing waves produced by the sum of waves traveling in opposite directions, shown as functions of the spatial coordinate at five different times. The sum is a spatial wave whose amplitude oscillates.
Lecture 8 Sound Waves Superposition and Standing Waves
Unit Waves Module Standing Waves [page Standing Waves
Standing Waves The lengths are related to each other by the ratios of whole integers. In fact, the Pythagoreans believed that this was a general principle of the universe: everything is related by the ratios of whole integers.
x t = f x ct c x g f g f Department of Physics USU
Chapter 16 Superposition and Standing Waves Physics 3
In this paper, we study the phenomenon of separation of traveling and standing waves in a one-dimensional rigid-walled circular duct. The underlying mechanism for separation, mode complexity, is linear and introduced here by a damped side branch representing an impedance discontinuity.
Separation of Traveling and Standing Waves in a ASME
MasteringPhysics 2.pdf Wave Equation Waves
Standing Wave I & II Prelab phys.utk.edu
The sum of two counter-propagating waves (of equal amplitude and frequency) creates a standing wave. Standing waves commonly arise when a boundary blocks further propagation of the wave, thus causing wave reflection, and therefore introducing a counter-propagating wave.
What is the difference between standing waves and
MasteringPhysics 2.pdf Wave Equation Waves
Superposition and Standing Waves If two or more traveling waves are moving through a medium, the resultant value of the wave function at any point is the algebraic sum of the values of the wave functions of the individual waves. Waves that obey this principle are called linear waves. In the case of mechanical waves, linear waves are generally characterized by having amplitudes much smaller
Lecture 8 Sound Waves Superposition and Standing Waves
Standing Waves UPSCALE
Using the “Clicker” Boston University Physics
Traveling Waves For the following activities, you will use both the Wave on a String PhET simulation and a long slinky or spring. 1. With the Oscillate button …
Standing and Traveling Waves Home Page-Dip.Informatica
STANDING WAVES In this experiment, standing waves will be observed in a vibrating string. The wavelengths of the waves and the tension in the string will be measured. From these measurements and the frequency of the wave, the mass per unit length of the string will be determined. The velocity of transverse traveling waves in a stretched string is given by v = Tμ where T is the tension in the
Standing and Traveling Waves Home Page-Dip.Informatica
Separation of Traveling and Standing Waves in a ASME
Physics 231 Standing Waves 4 The wiring diagram is shown in Fig. 2. The function generator is a source of AC voltage, which controls a transistor to drive 1-2 amps of current through the coil.
Physics 2A Chapters 15 Traveling Waves and Sound and 16
Hour 1 Traveling & Standing Waves Hour 2 Electromagnetic
Traveling And Standing Waves prohaustier.com
Thus, even though waves are traveling back and forth, the patterns of interference between all of these waves create this standing-wave pattern. Each of these potential patterns is called a mode of oscillation. In the simplest, fundamental mode, the whole string moves up and down together. In the next simplest, half of the string is moving up when the other half is moving down. In the next
Physics 3 Summer 1990 Lab 8 Standing and Traveling Waves
Standing Wave I & II Prelab phys.utk.edu
1537 Chapter 16 Superposition and Standing Waves Conceptual Problems 1 • [SSM] Two rectangular wave pulses are traveling in opposite directions along a string.
Standing Wave I & II Prelab phys.utk.edu
Physics 223 Experiment 1 Traveling Waves on a String
1/24/2017. MasteringPhysics 2.0: Problem Print View [ Problem View ] [ Creating a Standing Wave Learning Goal: To see how two traveling waves of the same frequency create a standing wave.
Physics 2A Chapters 15 Traveling Waves and Sound and 16
from the fact that two fermionic traveling waves with opposite direction, the kinetic energy of which is about 35 eV, form the bosonic standing wave, the kinetic energy of
Traveling Waves YouTube
Waves and Impedances on Transmission Lines Even though the waves are traveling in opposite directions, the interference pattern will be stationary with respect to the point of reflection, and will thus be a standing wave such as may be found on the strings of musical instrument (of course, these are also defined by a wave equation). The standing wave interference pattern is present both in
Chapter 5 Waves I Generalities Superposition & Standing
Standing Waves Rice University
Standing Waves – The Physics Hypertextbook
form of standing waves on a string that has boundary conditions that fall into the extremes (a flxed end or a free” end). In Section 4.6 we introduce damping, and we see how the amplitude of a wave decreases with distance in a scenario where one end of the string is wiggled with a constant amplitude. 4.1 The wave equation The most common example of a non-dispersive system is a string with
L5 Standing Waves Hamilton College
MIT 8.03SC Fall 2016 Textbook Chapter 8 Traveling Waves
Chapter 5 Waves I Generalities Superposition & Standing
it is possible to excite various standing wave modes in the wire. Using the apparatus provided, and shown schematically in Figure 2, design and carry out an experiment to verify the relation- ship of traveling wave speed,v, to tension, T, in the wire as described in Equation 1.
Standing And Traveling Waves On Transmission LinesGetting
MIT 8.03SC Fall 2016 Textbook Chapter 8 Traveling Waves
Superposition and Standing Waves • Superposition • Constructive and destructive interference • Standing waves • Harmonies and tone • Interference from two sources • Beats. 2 Principle of Superposition When two or more waves are simultaneously present at a single point in space, the displacement of the medium at that point is the sum of the displacement due to each individual wave
126-06 Standing Waves Stony Brook University
Physics 231 Standing Waves 4 The wiring diagram is shown in Fig. 2. The function generator is a source of AC voltage, which controls a transistor to drive 1-2 amps of current through the coil.
L5 Standing Waves Hamilton College